Lagune
Laguna di Lesina
Lesina lagoon is located in the southern Adriatic coast (Apulia region, Italy) on the northern coast of the Gargano promontory (41,88°N; 15,45°E; Figure 1). This ecosystem displays an extended and narrow shape elongated in the east to west direction and it is connected with the Adriatic Sea by means of natural and artificial canals interspersed with sand-dunes.
Cabras Lagoon System

Cabras lagoon is a shallow water body (mean depth 1.7 m) located on the west coast of Sardinia.
S'Ena Arrubia

S’Ena Arrubia Lagoon , located along the centre-western coast of Sardinia (39.83 °N and 8.57 °E), is included between plain of Arborea and coastal dune line. It is 1.2 Km2 wide, its mean depth is 40 cm and it is the residue of wider Sassu Pond, reclaimed in 1937.
Capo Feto Wetland

Capo Feto is a typical Mediterranean wetland (margi) located along the south-western coast of Sicily, 5 km west of Mazara del Vallo (37.68° N, 12.48° E). The study area is included in the inner surface of the Life-Nature project requalification financing to the UE. The marshland has a total extension of 1.4 Km2 and an average depth of 1.75 m. (Fig. 1). The catchment’s area of Capo Feto coastal zone shows the typical feature of wetland habitat.
Stagnone di Marsala

The Stagnone di Marsala is a 20 km2 extensive (about 1.8 km wide by 11 km long) lagoon on the North-western coast of Sicily (Italy). The lagoon has a northern narrow and shallow mouth to the sea (400 m wide, 0.3-0.4 m deep) and another wider and deeper to the south (1200 m wide, 1.0-1.5 m deep). At the eastern end of the northern opening a 20 m wide, 1 m deep channel was dredged, somehow enhancing the local flushing capability.
Rada di Augusta Lagoon

The “Rada di Augusta” is a wide natural bay which covers about 30 Km of the eastern coast of Sicily). Augusta Bay (Lat. 37,21°N - Long. 15,23° E) is situated between Capo Santa Croce and Punta Magnisi. In the past years, part of the bay has been walled up with breakwaters to form a vast harbour basin communicating with the sea through two narrow inlets (east and south).
Marinello Lakes

Capo Peloro

The Capo Peloro is a brackish system located on the north-eastern corner of Sicily, Italy. It consists of two basins, Ganzirri Lake (or Pantano Grande) and Faro Lake (or Pantano Piccolo), connected to each other by a channel. Both of them communicate with the Ionian Sea, moreover the Faro Lake occasionally exchanges water also with the Tyrrenian Sea.
Alimini Lake

Lake Alimini Grande is a salt-marsh ecosystem on the Adriatic coast of southern Italy (40.19°-40.22°N, 18.44°-18.46°E). Lake Alimini Grande has a surface area of 1.37km2, a sinuosity index of 2.29, an average depth of 1.5m and a volume of 2.1x106m3. It has an irregular shape (major axes:2.86km, minor axes:1.54km) and it is affected by dominant winds of the area along its major axes. It is connected with the sea through its mouth (length: 100m, width: 15m) and with a freshwater lake, Alimini Piccolo, through a natural canal 1.5km long, called the “Strittu”.
Taranto Sea

The Mar Piccolo of Taranto is located North of the town of Taranto (Fig. 1) and has a surface area of 20.72 km2. It is an inner, semi-enclosed basin with lagoon features divided by two rocky promontories into two inlets, called First Inlet (Primo Seno) and Second Inlet (Secondo Seno) which have a maximum depth of 13 and 8 m, respectively. The Mar Piccolo is connected with the Mar Grande through two channels, the Navigabile channel and the Porta Napoli channel, of which only the former is important for the water exchange in the basin. Tidal range does not exceed 30-40 cm.
Acquatina Lagoon

The Acquatina marsh area is a coastal marsh lake located on the Adriatic Sea shore of the Salento peninsula about 13 km North-East of Lecce (40.4425N – 18.2376E). It is linked to the nearby sea by a channel 15 m wide and 400 m long. The principal freshwater inputs are a lateral ramification of the Giammatteo canal (on the northern boundary of the lake) and rainfall. A long time ago the area was part of a system of marsh areas periodically invaded by the sea.
Torre Guaceto Lagoon

Torre Guaceto (Fig.1) is located in the Apulia region (ITALY), on the Adriatic coast, about 15 km North of Brindisi (40.7149°N-17.7989°E). The name of the area comes from the Arabic terms “GAW SIT” that means “freshwater site”. In 1981 the Torre Guaceto wetland was included in the List of Wetlands of International Importance (the "Ramsar List") under the Convention on Wetlands (Ramsar, Iran, 1971) and it was declared Special Protection Area by the Italian Minister of Agriculture.
Lagune Pontine

The four Pontine Lagoons are located ~100 km south of the city of Rome, in the territory of the National Park of Circeo. The specific names and surfaces, from north-west to south-east, are:
Genova Gulf

The Ligurian–Provencal Basin, together with the Gulf of Lions and the Catalan Sea, forms the North-western Mediterranean Basin. This region is characterized by a general cyclonic circulation fed by two distinct fluxes, one from the Tyrrhenian Sea through the Corsica Channel and the other from the northwestern side of Corsica. The two fluxes merge north of the island generating a very stable current that closely follows the sea bottom bathymetry along the Italian coast.
Porto di Genova
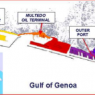
The Port of Genoa (44.40-44.43°N, 8.75-8.94°E) (Fig.1), located in the Gulf of Genoa, lays over a surface of 7 km2 along about 20 km of coastline; itswater depth varies between 9 and 15 m, with a maximum of 50 m in the Multedo Oil Terminal for super-tankers. The harbour receives domestic and industrial effluents both through the watercourses and through sewage treatment waters discharges. Therefore, significant amounts of nutrients are released in a semienclosed basin, producing a phosphorus and nitrogen enrichment.
Lagoon of Venice

The lagoon of Venice is the largest Italian Lagoonand one of the largest in Europe. It is located in the northern part of the Adriatic Sea (45.2° - 45.6°N, 12.2° and 12.6°E). Three narrow inlets connect thelagoon to the Adriatic sea, entailing a subdivision in three sub-basins, separated by two watersheds along which the intensity of the tidal currents is low.
The Pialassa Baiona Lagoon

The Pialassa Baiona is a lagoon located along the northern Adriatic Italian coast, between Ravenna harbour and the mouth of Lamone River (44.4673°- 44.5293° N 012.2375° - 012.2705° E, European Datum 1950; Fig. 1).
Valle Smarlacca Lagoon

The Valle Smarlacca lagoon is located on the North western Adriatic coast of Italy, in the Emilia-Romagna region. The lagoon is part of the Valli di Comacchio lagoon system(44.58°N, 12.23°E), a wide complex of shallow water impoundments (see the Valli di Comacchio information sheet). Valle Smarlacca is located in the southeast corner of the Valli di Comacchio, close to the Reno River. It has a surface area ofabout 2 km and a mean water depth of 0.8 m.
Laguna di Orbetello

The Orbetello lagoon is located in southern Tuscany (Italian West Coast), between 42°25’28” and 42°28’57” lat. North and between 11°10’6” and 11°16’45” long. East, and covers a total area of 25.25 km. This lagoon consists of two communicating basins known as Ponente (West) and Levante (East) measuring in area respectively 15.25 and 10.00 km (values according to Travaglia & Lorenzini, 1985, modified as a result of recent filling operations), with an average depth of about 1 m. The tidal range is small and varies between 0.1 and 0.45m.
The Orbetello Lagoon System

S'Ena Arrubia

S’Ena Arrubia Lagoon , located along the centre-western coast of Sardinia (39.83 °N and 8.57 °E), is included between plain of Arborea and coastal dune line. It is 1.2 Km2 wide, its mean depth is 40 cm and it is the residue of wider Sassu Pond, reclaimed in 1937.
Capo Feto

Capo Feto is a typical Mediterranean wetland (margi) located along the south-western coast of Sicily, 5 km west of Mazara del Vallo (37.68° N, 12.48° E). The study area is included in the inner surface of the Life-Nature project requalification financing to the UE. The marshland has a total extension of 1.4 Km2 and an average depth of 1.75 m. (Fig. 1). The catchment’s area of Capo Feto coastal zone shows the typical feature of wetland habitat.
Stagnone di Marsala

The Stagnone di Marsala is a 20 km2 extensive (about 1.8 km wide by 11 km long) lagoon on the North-western coast of Sicily (Italy). The lagoon has a northern narrow and shallow mouth to the sea (400 m wide, 0.3-0.4 m deep) and another wider and deeper to the south (1200 m wide, 1.0-1.5 m deep). At the eastern end of the northern opening a 20 m wide, 1 m deep channel was dredged, somehow enhancing the local flushing capability.
Rada di Augusta Lagoon

The “Rada di Augusta” is a wide natural bay which covers about 30 Km of the eastern coast of Sicily). Augusta Bay (Lat. 37,21°N - Long. 15,23° E) is situated between Capo Santa Croce and Punta Magnisi. In the past years, part of the bay has been walled up with breakwaters to form a vast harbour basin communicating with the sea through two narrow inlets (east and south).
Laghetti di Marinello

The Marinello coastal system is a small littoral area located in the Patti Gulf (Messina, Italy), behind the Tindari Cliff (38,13°N – 15,05°E), that currently includes five little deep ponds whose shape, number and dimensions are continuously changed by the rapid evolution of coastal morphology. At present, the system covers an area of approximately 697,000 m2.
Capo Peloro

The Capo Peloro is a brackish system located on the north-eastern corner of Sicily, Italy. It consists of two basins, Ganzirri Lake (or Pantano Grande) and Faro Lake (or Pantano Piccolo), connected to each other by a channel. Both of them communicate with the Ionian Sea, moreover the Faro Lake occasionally exchanges water also with the Tyrrenian Sea.
Lago Alimini Grande

Lake Alimini Grande is a salt-marsh ecosystem on the Adriatic coast of southern Italy (40.19°-40.22°N, 18.44°-18.46°E). Lake Alimini Grande has a surface area of 1.37km2, a sinuosity index of 2.29, an average depth of 1.5m and a volume of 2.1x106m3. It has an irregular shape (major axes:2.86km, minor axes:1.54km) and it is affected by dominant winds of the area along its major axes. It is connected with the sea through its mouth (length: 100m, width: 15m) and with a freshwater lake, Alimini Piccolo, through a natural canal 1.5km long, called the “Strittu”.
Mar di Taranto

The Mar Piccolo of Taranto is located North of the town of Taranto (Fig. 1) and has a surface area of 20.72 km2. It is an inner, semi-enclosed basin with lagoon features divided by two rocky promontories into two inlets, called First Inlet (Primo Seno) and Second Inlet (Secondo Seno) which have a maximum depth of 13 and 8 m, respectively. The Mar Piccolo is connected with the Mar Grande through two channels, the Navigabile channel and the Porta Napoli channel, of which only the former is important for the water exchange in the basin. Tidal range does not exceed 30-40 cm.
Acquatina Lagoon

The Acquatina marsh area is a coastal marsh lake located on the Adriatic Sea shore of the Salento peninsula about 13 km North-East of Lecce (40.4425N – 18.2376E). It is linked to the nearby sea by a channel 15 m wide and 400 m long. The principal freshwater inputs are a lateral ramification of the Giammatteo canal (on the northern boundary of the lake) and rainfall. A long time ago the area was part of a system of marsh areas periodically invaded by the sea.

